Net Operating Income (NOI) Explained

Understanding Net Operating Income (NOI) is crucial for investors looking to assess the profitability of commercial real estate. NOI helps determine a property’s financial performance by measuring its revenue after operating expenses—without factoring in debt payments. Whether you’re evaluating a new investment or optimizing your portfolio, mastering NOI is essential for making informed, data-driven decisions.
In this guide, we’ll break down the NOI formula, explain how to calculate it, and discuss what constitutes a “good” NOI in real estate.
What is NOI (Net Operating Income)?
Net Operating Income (NOI) is a fundamental metric used in commercial real estate to measure the profitability of income-generating properties. It is the sum of the property’s rental income and ancillary income, subtracted by its direct operating expenses.
NOI is a before-tax figure that excludes principal and interest payments on loans, capital expenditures, depreciation, and amortization. It is a critical metric used to analyze the profitability of an asset or an investment after subtracting operating expenses from the income generated by the property.
Net Income Vs. Net Operating Income Approach
When comparing the metrics used to assess the profitability of income-generating properties, net income and Net Operating Income (NOI) are commonly used. Net income is the total income generated by a property after deducting all expenses, including financing costs.
On the other hand, NOI provides a more accurate picture of a property’s profitability as it takes into account the property’s operating expenses and cash flow. This makes NOI a crucial metric for evaluating the performance and value of income-generating properties, allowing for informed investment decisions and a better understanding of a property’s financial health.
Capitalization Rates and NOI
Capitalization rate (Cap Rate) is a crucial metric used in real estate investment to determine the rate of return on a property based on its expected income. It is calculated by dividing the property’s Net Operating Income (NOI) by its current market value.
Cap Rate is used to estimate an investor’s potential rate of return on their investment in a property, assuming they paid all cash for the property, based on the property’s projected income. The lower the Cap Rate, the lower the risk of the investment. Understanding the relationship between NOI and Cap Rate is essential for evaluating the profitability and potential return of income-generating properties.
NOI Formula
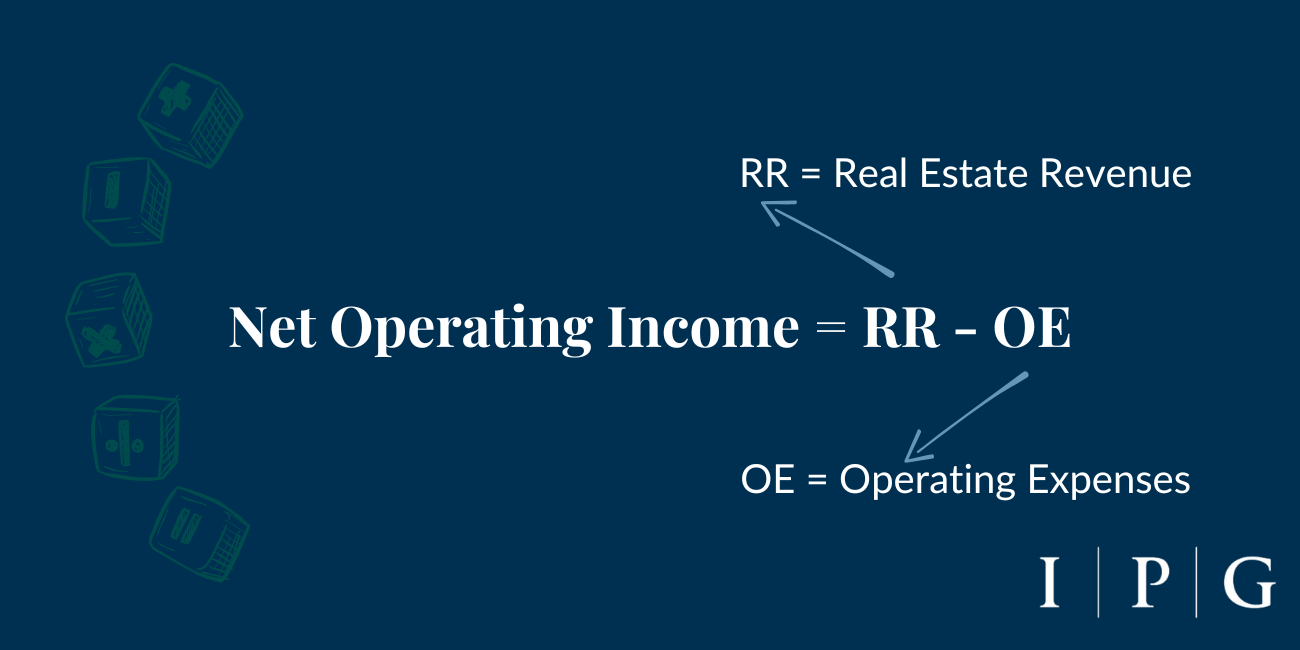
Net Operating Income (NOI) is a crucial metric used in real estate investment to determine the profitability of income-generating properties.
It is calculated by subtracting the property’s operating expenses from its total income. NOI is a before-tax figure that excludes principal and interest payments on loans, capital expenditures, depreciation, and amortization.
The NOI formula is the foundation for assessing the potential income from an investment property, making it an essential component of real estate investment analysis. Understanding the key components and considerations in the NOI calculation is vital for investors and industry professionals to make informed decisions and evaluate the performance of income-generating properties.
NOI Calculation: How to Calculate NOI?
Calculating Net Operating Income (NOI) involves understanding the revenue a property generates after removing all direct operating expenses. NOI is a crucial metric, serving as a standardized indicator of a property’s profitability, which is essential for analyzing investment opportunities.
NOI is particularly valuable because it reveals the historical profitability of a property investment, offering insights into its profit potential on a forward-looking basis. This makes NOI not just a practical measure for evaluating the current profitability of a property but also an effective tool for comparing different property investments. It provides a more ‘apples-to-apples’ comparison by excluding financing costs, debt services, and capital expenditures from its calculation.
For Example
Consider a condo building with the following financial profile:
Revenue Breakdown:
- Rental Income: $20,000
- Parking Fees: $5,000
- Laundry Machines: $1,000
Total Revenue (TRR): $26,000
Operating Expenses Breakdown:
- Property Management Fees: $1,000
- Property Taxes: $5,000
- Repair and Maintenance: $3,000
- Insurance: $1,000
Total Operating Expenses (TOE): $10,000
Using this data, the Net Operating Income (NOI) for the condo building would be calculated as follows:
NOI = RR – OE
NOI = $26,000 – $10,000
NOI = $16,000
So in this example, the condo building generates a Net Operating Income of $16,000.
What is a Good NOI for a Rental Property?
Determining a “good” Net Operating Income (NOI) for a rental property can be subjective, as it depends on factors like property type, location, and the real estate market’s condition. Generally, a rental property is seen favorably if it has a positive NOI that surpasses similar properties, indicating profitability.
In contrast, a negative NOI suggests that the property’s operational costs exceed its income, marking it as unprofitable. To assess a rental property’s value using NOI, investors typically compare it to the property’s market value or purchase price.
What is a Good NOI Margin?
To effectively compare different properties, Net Operating Income (NOI) is often standardized into a margin. The NOI margin is a measure of a property’s operating efficiency and is found by dividing NOI by the total property revenue and then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
This margin essentially shows what portion of every dollar earned in revenue is retained as net operating profits (NOI). A higher NOI margin indicates a larger portion of revenue is converted into NOI, reflecting operational efficiency. Conversely, a lower NOI margin suggests operational inefficiency.
However, to gain meaningful insights, it’s important to compare the NOI margin with similar properties in terms of type, class, and location, rather than analyzing it in isolation. This comparison provides a relative benchmark for a more comprehensive analysis.
The Bottom Line
Net Operating Income (NOI) is a key measure of a property’s profitability, calculated by deducting operating expenses from total revenue. The greater the revenue and lower the expenses, the more profitable the property. NOI essentially indicates whether the income from a property justifies the costs of owning and maintaining it.




